Egypt lies in the northern part of Africa. It borders both the Mediterranean Sea and the Red Sea. The Nile River makes the land green, while the rest of Egypt is covered with desert. Mount Catherine is a large mountain with multiple uses. Temperatures in Egypt are generally very high. The country is famous for its ancient civilization, which began around 3100 BC along the banks of the Nile River. For this reason, Egyptians consider their country the “Gift of the Nile.”
Before Egyptian Civilization
Stone Age
Human life in Egypt began during the Paleolithic period, around 500,000 BC. This era continued until approximately 10,000 BC. Archaeologists have discovered traces of along the Nile who gathered fruits and hunted animals. They also used hand-made stones, awls, arrowheads, knives, and axes. These early humans relied on hunting and wild fruits and often lived in caves.
New Stone Age
Experts believe that Egyptians began agricultural life between 6000 and 4000 BC. During the Nile River floods, people started farming and raising animals. However, historians debate which civilization first practiced agriculture: Egyptian, Mesopotamian, or Indus. Scholars have different opinions on this topic.
_Read about Mesopotamia Civilization.

Pre-Dynastic Period
This period lasted approximately from 4000 BC to 3100 BC. During this era, small states formed within the region. Upper Egypt developed in the south, while Lower Egypt formed in the north. Experts suggest that the first signs of social organization and kingship emerged during this period. Around 3100 BC, Pharaoh Narmer, also called Menes, united Upper and Lower Egypt. This marked the beginning of the glorious era of Egyptian civilization.
__Read about Judaism which was initiated from Egypt.
Egyptian Civilization
For thousands of years, Egypt divided into two parts: Upper Egypt above the Nile and Lower Egypt below it. The crown of Upper Egypt was white, while the crown of Lower Egypt was red. Around 3250 BC, Pharaoh Narmer conquered both parts of Egypt and founded the First Dynasty. Some historians consider Narmer and Menes to be the same person, while others treat them as separate individuals. Narmer made Thebes his capital. A statue of this pharaoh’s face is displayed in the London Museum. During this time, Egyptians worshiped the god Min.

Political Situation of Egypt
For thousands of years, Egyptians completely obeyed the pharaohs. These rulers combined political and religious authority. Egyptians considered pharaohs as the children of God on Earth, and at times, as divine themselves. People believed the pharaoh’s words represented God’s words. The pharaoh personally owned all of Egypt. Ordinary people had no personal status before him. Egyptians thought people were born to serve God and the pharaoh. The pharaoh controlled every aspect of their lives.
When a pharaoh died, Egyptians equated his death with the death of God. They buried him with great honor. The pharaoh’s body went into a coffin and was immersed in honey to ensure safe passage during his second birth. Then, the coffin was placed in a pyramid, which served as a palace for the pharaoh. Pyramids included thrones, resting rooms, guest spaces, and burial sites for relatives. After construction, pyramids were sealed with stones and secret doors.
Initially, the Egyptian language had no word for “pharaoh.” Instead, people used “nswt” (nesut) or “hm ntr” (hem-netjer) to refer to the king.

Ancient Egypt (2686–2181 BC)
This era is also known as the Age of the Pyramids. Egyptians built the great pyramids of Giza during this period. Some famous pharaohs include:
Khufu: He built the Great Pyramid, employed hard labor, and increased taxes. Some historians describe him as a harsh ruler.
Khafre: He strengthened religious influence in Egypt.
Menkaure: He maintained stable governance and was known for his justice and mercy.
Middle Kingdom (2055–1650 BC)
Before this period, Egypt experienced chaos for a century. Later, reforms improved the conditions of the people. Literature, arts, and crafts flourished during this period. Famous pharaohs include:
Amenemhat I: He introduced plans to improve agriculture and boost the economy.
Senusret II: He emphasized justice and law and involved people in military campaigns.

New Kingdom (1550–1070 BC)
Egypt reached its peak of power and glory during this era. Pharaohs launched major military campaigns and expanded the empire. They also constructed monumental structures, such as the Abu Simbel temples. Famous pharaohs of this period include:

Hatshepsut: A female pharaoh, she became famous for trade and construction. She brought peace, prosperity, and benefits to her subjects.
Akhenaten: He promoted monotheism, which caused religious unrest.
Tutankhamun: He restored the old religious system.
Ramses II: Known as the most famous and powerful pharaoh.
Cleopatra: The last pharaoh, she allied with Rome to protect her kingdom. Despite her efforts, wars with Rome challenged her rule.
Religious Situation of Egyptian Civilization
Early Egyptians worshiped many gods. They recognized at least two thousand deities, including eight major creator gods. Each claimed to be the universe’s creator and owner. Most gods used the words “be & it is” to create the world. The female goddess Neith was also part of the group of creator gods.
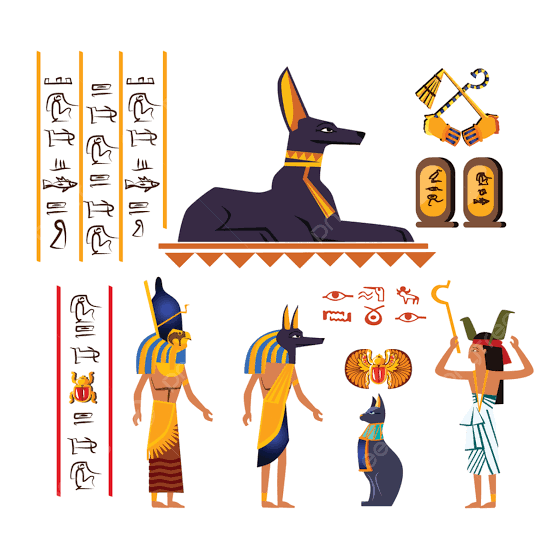
Egyptian Gods of Ancient Egypt
The First Creator God: Atum
In the city of Heliopolis in Lower Egypt, the god Atum was considered the creator and king of the universe. According to Egyptian beliefs, he created himself as the first god. Many statues depict this god. Furthermore, Atum created the god Athena. In addition, he gave birth to the god Shu and the goddess Nefnut.
In Egyptian mythology, it was believed that the god Nefnut and the god Geb had an illicit relationship. Therefore, Shu separated them from each other. However, due to their union, four other gods and goddesses were born:
- Osiris
- Isis
- Set
- Nephthys

The Second Creator God: Geb
Egyptians believed that Geb laughed loudly. Consequently, his laughter caused earthquakes on the earth. They also called him the father of snakes. Moreover, they sometimes depicted Geb as a sheep or a cow.
The Third Creator God: Ptah
Ptah was the god of the city of Memphis, where people considered him the creator god. Egyptians believed that his spirit resided in the great temple of Memphis. This god spoke two words, “Be & it is,” and created the universe. In addition, scholars believe that Ptah was the son of Nun and the god Nunnet.

People described the attributes of Ptah as follows:
- Beautiful-faced
- Guardian of truth
- Giver of justice
- Rememberer of those who worship him
- Leader of all customs and traditions
- Owner of eternal existence or immortality
Moreover, Egyptians built large temples for Ptah outside of Egypt.
The Fourth Creator God: Amun
People in the Egyptian city of Thebes believed that Amun created the universe. They also believed that he had power over everything.
The Fifth Creator God: Ra
Egyptians considered Ra the creator of the entire universe. In fact, the earth, sky, moon, and the entire world obeyed his command. When he spat, humans were born on earth. Ra was the sun god. First, he created himself, and then he spat while saying the words “Be & it is,” creating the universe. Furthermore, Egyptians sacrificed cows in his name.
The Three Daughters of Ra
- Bastet: Called the cat of Ra
- Sekhmet: Known as the cow of Ra
- Hathor: Recognized as the eye of Ra
According to Egyptian mythology, Ra felt pleased with his work. Consequently, all gods welcomed him to the sky and received him in paradise. After a feast, the gods gave Ra their powers and attributes. As a result, Ra became known as Amun Ra.
Other Egyptian Gods
God Iabet
Iabet was considered the second god of birth.
God Hu
Hu acted as the keeper of the words “Be & it is.”
God Khenmu
Khenmu created human statues from Nile soil and placed them inside the special organ of a woman to create man.
God Bastet
Bastet sometimes appeared as a cat or a lion. Moreover, Egyptians made thousands of statues in his honor. After a cat died, they buried it with royal rituals. In fact, more than 300,000 statues of such cats exist.
God Sekhmet
Sekhmet protected people from war, destruction, and plague. Egyptians depicted his face as a cat or a lion. In addition, the sun shone above his head. He wore a blood-red robe and always thirsted for blood. This god resembles some Hindu gods.
_Read about Hinduism.
Goddess Hathor
Hathor represented sex, music, dance, and love. She married many gods, including Ra, and bore countless children. Egyptians sometimes depicted her as a cow, a beautiful woman, a serpent, or a lioness. Furthermore, she enjoyed wide worship. Annual festivals honored her, and shrines existed in Canaan and Sudan.
Writer : GM Leghari














